Java
Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language that is designed to be platform-independent, thanks to its "write once, run anywhere" philosophy. This means that code written in Java can run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) installed, making it versatile for various applications.
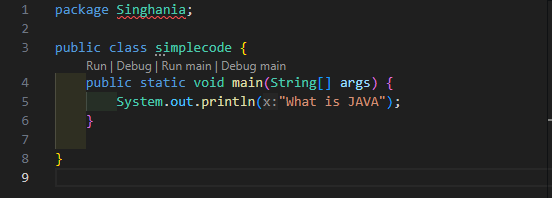
Java code for beginner....
OUTPUT:-This is a results What is JAVA
Key features of Java include:
1. **Object-Oriented**: Java is based on the principles of object-oriented programming (OOP), which helps in organizing complex programs through concepts like classes and objects.
2. **Platform Independence**: Java code is compiled into bytecode, which can be executed on any machine that has the JVM, regardless of the underlying hardware and operating system.
3. **Automatic Memory Management**: Java has built-in garbage collection, which helps manage memory by automatically reclaiming memory that is no longer in use.
4. **Rich Standard Library**: Java provides a comprehensive standard library that includes utilities for data structures, networking, file I/O, and much more.
5. **Strongly Typed**: Java enforces strict type checking at both compile-time and runtime, which can help catch errors early.
Java is widely used for building enterprise applications, web applications, mobile apps (especially Android), and more. Its robustness and security features have made it a popular choice in many industries.
Sure! Here’s a deeper dive into Java and its ecosystem:
### Core Concepts
1. **Syntax**: Java's syntax is similar to C and C++, making it familiar to many developers. It uses semicolons to end statements and curly braces to define code blocks.
2. **Classes and Objects**: Everything in Java is based on classes and objects. A class defines a blueprint for objects, which are instances of classes. This encapsulation allows for better organization and modularity in code.
3. **Inheritance**: Java supports inheritance, allowing one class to inherit fields and methods from another. This promotes code reuse and establishes a hierarchical relationship between classes.
4. **Polymorphism**: Java allows methods to perform differently based on the object calling them. This can be achieved through method overloading (same method name, different parameters) and method overriding (subclass providing a specific implementation).
5. **Interfaces**: An interface in Java is a reference type that can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static methods, and nested types. It’s a way to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance.
### Java Ecosystem
1. **Java Development Kit (JDK)**: The JDK is a software development environment that provides the tools needed to develop Java applications, including the Java Compiler (javac), the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and various libraries.
2. **Java Runtime Environment (JRE)**: The JRE is the part of the Java environment that runs Java applications. It includes the JVM, core libraries, and other components needed to execute programs written in Java.
3. **Java Virtual Machine (JVM)**: The JVM is an engine that provides a runtime environment to execute Java bytecode. It converts bytecode into machine code, enabling Java's platform independence.
4. **Frameworks and Libraries**:
- **Spring**: A powerful framework for building enterprise applications, particularly in web development.
- **Hibernate**: An object-relational mapping (ORM) framework that simplifies database interactions.
- **JavaFX**: A library for building rich internet applications with a modern UI.
- **Maven/Gradle**: Build automation tools that manage project dependencies and build processes.
### Applications of Java
1. **Enterprise Applications**: Java is commonly used for large-scale enterprise applications due to its robustness and scalability.
2. **Mobile Development**: Java is the primary language for Android development, supported by frameworks like Android SDK.
3. **Web Applications**: Java is widely used in server-side applications with technologies like JavaServer Faces (JSF), Servlets, and JSP.
4. **Embedded Systems**: Java can also be used in embedded systems and IoT applications.
5. **Big Data Technologies**: Tools like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark utilize Java for processing large datasets.
### Community and Support
Java has a large and active community, which means plenty of resources, forums, and libraries are available for developers. Java's longevity (first released in 1995) has also contributed to a wealth of tutorials, documentation, and frameworks.
### Versioning and Updates
Java has undergone several updates over the years, with major versions introducing new features and enhancements. The release cycle has moved to a more regular cadence, with new versions coming out every six months. Key recent features include:
- **Java 8**: Introduced lambda expressions, the Stream API, and the new Date and Time API.
- **Java 11**: A Long-Term Support (LTS) version that included improvements like new HTTP client and enhancements to the String API.
- **Java 17**: Another LTS version that added pattern matching for `instanceof`, sealed classes, and various performance improvements.
### Conclusion
Java remains a cornerstone of the programming world, valued for its reliability, scalability, and widespread use across industries. Whether you're building web applications, mobile apps, or enterprise solutions, Java offers the tools and community support to get the job done. If you have specific areas or topics about Java you'd like to explore further, feel free to ask!
Absolutely! Let’s explore some additional aspects of Java, including its history, features, performance, best practices, and emerging trends.
### History of Java
- **Origins**: Java was developed by Sun Microsystems in the early 1990s, originally designed for interactive television. The first public release was in 1995.
- **Key Milestones**:
- **Java 1.0 (1996)**: The first official release, establishing Java's "write once, run anywhere" capability.
- **Java 2 (1998)**: Introduced major features like the Swing GUI toolkit and the Java 2 Platform, which included core APIs.
- **Java 5 (2004)**: Brought significant updates like generics, annotations, enumerated types, and the enhanced for loop.
- **Java 8 (2014)**: Marked a significant evolution with the introduction of lambdas, streams, and the new Date and Time API.
- **Java 9 (2017)**: Introduced the module system (Project Jigsaw) and JShell, an interactive REPL tool.
### Features of Java
1. **Multi-threading**: Java supports multi-threading, allowing concurrent execution of two or more threads for maximum utilization of CPU resources.
2. **Exception Handling**: Java provides a robust exception handling mechanism, which helps in managing runtime errors and maintaining the normal flow of application execution.
3. **Security Features**: Java has built-in security features such as the Java Security Manager, bytecode verification, and a security architecture that protects against threats like unauthorized access.
4. **Rich API**: The Java API provides a wide array of classes and interfaces for various tasks, from networking and I/O operations to data structures and algorithms.
5. **Java Annotations**: Annotations provide metadata information about the program and can be used for configuration, code analysis, and documentation.
PDF DOWNLOAD..
CodinG TutoriaL
JAVA SIMPLE CODE..
### Performance
Java’s performance has improved significantly over the years:
- **Just-In-Time Compilation (JIT)**: The JVM uses JIT compilation to convert bytecode into native machine code at runtime, enhancing performance.
- **Garbage Collection**: Java's garbage collectors have evolved, with various algorithms (like G1, ZGC, and Shenandoah) optimizing memory management and reducing pause times.
- **Performance Tuning**: Developers can optimize performance through various techniques, such as tuning JVM options, using efficient data structures, and profiling applications.
### Best Practices
1. **Use Proper Naming Conventions**: Follow Java naming conventions (e.g., classes in CamelCase, methods in camelCase) for better readability and maintainability.
2. **Keep Code Modular**: Break down code into smaller, reusable methods and classes to enhance readability and testability.
3. **Use Interfaces and Abstract Classes**: This promotes loose coupling and allows for easier changes in the future.
4. **Optimize Exception Handling**: Use exceptions wisely, catching only what you need and avoiding exceptions in performance-critical sections of code.
5. **Document Your Code**: Use Javadoc comments to provide clear documentation for classes and methods.
6. **Test Thoroughly**: Implement unit testing (using frameworks like JUnit) and integration testing to ensure code quality and reliability.
### Emerging Trends
1. **Microservices Architecture**: Java is increasingly used in microservices architecture, allowing developers to build applications as a suite of small, independent services.
2. **Reactive Programming**: Frameworks like Spring WebFlux and Project Reactor enable reactive programming in Java, allowing developers to build responsive and scalable applications.
3. **Cloud-Native Development**: With the rise of cloud computing, Java applications are being designed to leverage cloud services, often using containerization technologies like Docker and orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
4. **Machine Learning and AI**: Java is finding its place in machine learning and AI, with libraries like Deeplearning4j and Weka providing tools for data analysis and model building.
5. **Serverless Computing**: Java is increasingly used in serverless architectures, allowing developers to write functions that run in response to events without managing server infrastructure.
### Community and Resources
- **OpenJDK**: The open-source implementation of the Java Platform, which is a key resource for developers.
- **Java Community Process (JCP)**: A formalized mechanism for developing standard technical specifications for Java technology.
- **Online Courses and Tutorials**: Many platforms offer courses on Java, such as Coursera, Udacity, and Codecademy.
- **Conferences**: Events like JavaOne and Devoxx provide networking opportunities and insights into the latest developments in the Java ecosystem.
### Conclusion
Java's rich history, robust features, and large ecosystem make it a powerful choice for a variety of programming tasks. Its adaptability to new trends and technologies ensures that it remains relevant in a rapidly evolving landscape. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, Java offers a vast array of tools and resources to help you succeed. If you have any specific questions or areas you'd like to explore further, just let me know!